- SAP GUI for windows is SAP's windows based client for accessing all SAP Dynpro functionality.
- It is also provided access to all the SAP product and software components for example SAP CRM, SAPSCM, SAP ERP Solutions Manager, XI, BW etc.
- The SAP GUI is used to access all the customer systems irrespective of operating system and database.
- SAP GUI is downward compatible i.e the latest release of the SAP GUI software (such as SAPGUI for windows 7.40) works with all previous SAP product releases thus getting the feature of latest GUI.
- It provides SAP GUI for JAVA which is SAP's unified front end for multiple platforms (OS x, Linux and windows).
- It is the most interactive and communicative GUI where user submit the requests.
- It is role based, menu based and transaction based GUI.
- SAP GUI for HTML is used to access the SAP content over the web.
- It is easily customisable to change colours, themes etc.
- It is ergonomically designed to change the fonts and their size.
- Provides network settings to suppress GUI Elements using a low speed connection.
- Provide favorites to reduce the navigation levels.
- Provides set start transaction to directly navigate to the transactions.
- Supports secure network connectivity (SNC) to connect to SAP system without any password.
- The Logon entried are store in SAPLogon.iri and SAPUILandscape.xml.
- Same GUI will be used to access the SAP systems with multiple languages.
- Same GUI supports multiple Interfaces
Sunday, August 14, 2016
SAP GUI features:
4) Netweaver Business client 3.0/4.0/5.0 (SAP Business client 6.0)
SAP businessclient 6.0 is the latestchild inthe SAP business client family formerly known as SAP Netweaver business client (NWBC). It is a rich user interface desktop client 6.0 provides the following:
Role based single entry point to SAP business applications efficient, intuitive and complete user experience with integration of various UI technologies in particular SAP GUI Web Dynpro. ABAP and SAP Fiori step by step approach for achieving an SAP fiori user experience on windows desktops.
Netweaver Business client for HTML: it is representation of SAP over the web using Web dynpro ABAP screens or JAVA screens.
a) IT requires activation of 'nwbc' service in sicf.
b) Setup a fully qualified hostname in RZ10 using parameter icm/host_name_full
c) Check whether parameter icm/server_port_o is set with port and port and protocol
http://hostname:8000/nwbc isused to navigate to NWBC for HTML
5)SAP FioriClient:
It is based on UI technologies with ATOM protocol, JSON, WSDL and SOAP Languages. it provides a file based GUI which will be querying the database and providing the access to various Front end devices such as desktop, webtops, mobile devices, tablets and hand held devices. It requires deployment of SAP Netweaver gateway and UI Specific add-on. (Ex: ERP, CRM, SRM, SCM, GRC)
6) SAP GUI for Java products like enterprise portal:
Enterprise portal XI,MI, SLD (System landscape directory) and SAP Java engine are built using java language. These applications are accessed on the web using port 50000.
Process of Activating WebGUI
1) Execute Transaction "SITSPMON" which is available onlyl from basis versions 640 and above.
System ==> Status ==> Magnifying glass ==> check the basis release which should be 640 and above.
2) SITSPMON (SAP Internet Transaction Server Process Monitor):
It is used to provide the inbuilt ITS services to SAP System.
a) Check whether status light is "GREEN" with ITSPE is OK.
b) Check whether the parameter itsp/enable=1 (If it is set to '0' internet services are disabled)
3) Execute SMICM (Internet Communication Manager):
It is a service which is active from BASIS 640. It is used handle the web requests check whether ICM status is Green and Running.
4) Activate Internet Communication frame work services based on requirements. Execute transaction "SICF"
/sap/public/bc
/sap/public/bc/ur
/sap/public/bc/its/mimes
/sap/public/ping
/sap/bc/gui/sap/its/webgui
Right click on each of the services and activate the service (There are services like BW, CRM, SRM, Solman, KW etc are activated based on requirements)
5) Execute "SE80" and publish the services
Select internet service => system (right click) => public complete service
Select Internet service => Web GUI (right click)=> Publish complete service
6) To check the hostname, Port and protocol that is going to be used on the web.
Execute SMICM ==> Men Goto==> Services==>
Execute SMICM==> Menu Goto==> Parameters ==> Display
Note: generally the hostname should be fully qualified on the web.
So configure thehost by using parameter intransaction RZ10 using parmeter icm/host_name_full=abs.co.in
set the ports using parameter
icm/server_port_0=PROT=HTTP,PORT=8000
icm/server_port_1=PROT=SMTP,PORT=25
icm/server_port_2=PROT=https,PORT=443
Fully qualified host name means the hostname with atleast two dots(.) The parameters are configured in RZ10.
System ==> Status ==> Magnifying glass ==> check the basis release which should be 640 and above.
2) SITSPMON (SAP Internet Transaction Server Process Monitor):
It is used to provide the inbuilt ITS services to SAP System.
a) Check whether status light is "GREEN" with ITSPE is OK.
b) Check whether the parameter itsp/enable=1 (If it is set to '0' internet services are disabled)
3) Execute SMICM (Internet Communication Manager):
It is a service which is active from BASIS 640. It is used handle the web requests check whether ICM status is Green and Running.
4) Activate Internet Communication frame work services based on requirements. Execute transaction "SICF"
/sap/public/bc
/sap/public/bc/ur
/sap/public/bc/its/mimes
/sap/public/ping
/sap/bc/gui/sap/its/webgui
Right click on each of the services and activate the service (There are services like BW, CRM, SRM, Solman, KW etc are activated based on requirements)
5) Execute "SE80" and publish the services
Select internet service => system (right click) => public complete service
Select Internet service => Web GUI (right click)=> Publish complete service
6) To check the hostname, Port and protocol that is going to be used on the web.
Execute SMICM ==> Men Goto==> Services==>
Execute SMICM==> Menu Goto==> Parameters ==> Display
Note: generally the hostname should be fully qualified on the web.
So configure thehost by using parameter intransaction RZ10 using parmeter icm/host_name_full=abs.co.in
set the ports using parameter
icm/server_port_0=PROT=HTTP,PORT=8000
icm/server_port_1=PROT=SMTP,PORT=25
icm/server_port_2=PROT=https,PORT=443
Fully qualified host name means the hostname with atleast two dots(.) The parameters are configured in RZ10.
Saturday, August 13, 2016
Installation Part:
1) SAP GUI for windows:
Download the software using SAP download manager and extract it toa folder. Navigateto the installation executables and use "setupall.exe".
Select the GUI components that need to be installed (deselect the components that need to be uninstalled and continue the installation/ uninstallation.
some of the components may need some additional components like.net frame work etc.
SAP GI for windows provides an option to select the CRM, SRM, SCM dependents, ECL (Engineering Client Viewer for 2D, 3D etc)
It alsoprovides knowledge management, BW, Netweaver Business client etc.
The Logon entries are maintained in saplogon.ini (older versions), SapUILandscape.xml. These files can be stored accessed by all the presentation servers.
2)SAP GUI for JAVA:
It required a compatible version of JAVA which is specific to operating system.
Download the OS specific SAP GUI for Java software from SAP marketplace. Generally it is around 40MB.
Use command "Java - jar PlatinGUI<rel><OS>_nnn.JAR"
It is installed by default in /opt/SAPClients/SAPGUI/bin folder to initialize SAPGUInavigate to the above folder and use /guilogon..
3)SAP GUI for HTML:
It is a representation of classic GUI over the browser using HTML. It requiredinternet transaction server to convert the classic content to web content.
Download the software using SAP download manager and extract it toa folder. Navigateto the installation executables and use "setupall.exe".
Select the GUI components that need to be installed (deselect the components that need to be uninstalled and continue the installation/ uninstallation.
some of the components may need some additional components like.net frame work etc.
SAP GI for windows provides an option to select the CRM, SRM, SCM dependents, ECL (Engineering Client Viewer for 2D, 3D etc)
It alsoprovides knowledge management, BW, Netweaver Business client etc.
The Logon entries are maintained in saplogon.ini (older versions), SapUILandscape.xml. These files can be stored accessed by all the presentation servers.
2)SAP GUI for JAVA:
It required a compatible version of JAVA which is specific to operating system.
Download the OS specific SAP GUI for Java software from SAP marketplace. Generally it is around 40MB.
Use command "Java - jar PlatinGUI<rel><OS>_nnn.JAR"
It is installed by default in /opt/SAPClients/SAPGUI/bin folder to initialize SAPGUInavigate to the above folder and use /guilogon..
3)SAP GUI for HTML:
It is a representation of classic GUI over the browser using HTML. It requiredinternet transaction server to convert the classic content to web content.
Saturday, August 6, 2016
Types of Presentation Layers
Types of Presentation Layers:
- SAP GUI for windows
- SAP GUI for JAVA
- SAP GUI for HTML
- Netweaver business client (UI)
- Fiori Launch Pad (UX)
- SAP WEB Dynpro JAVA (web based)(outdated)
1) SAP GUI for Windows:
It is a client software which designed to work on windows platforms.
It of size around 1.2 GB. It is the most convenient GUI for developers, functional consultants, end user community and business process owners.
Download the SAP GUI for windows from
http://service.sap.com/swdc ==> Installations and upgrades
==> SAP front end components ==> SAP GUI for windows 7.40
==>. select and download
2) SAP GUI for JAVA Environment:
SAP's unified frontend for multiple platforms (Linux and Windows). It is based on a platform independent architecture and Java implementation.
It required platform specific JAVA to run SAP GUI for JAVA. SAP GUI for JAVA 7.40 is designed to run with SAP systems based on SAP Netweaver application server 7.40 and earlier versions which are still supported by SAP. Current version of SAP GUI for JAVA is SAP GUI 740 PL 8. It's size is approximately 40 MB.
3) SAP GUI for HTML:
It is a browser based GUI which converts the classic GUI screens into WEB Screens using in built internet transaction server. It required an Host Name and HTTP port number to access the SAP products.
4) SAP Business Client:
Earlier its called as Netweaver business client.. It provides a client on the desktop or a web client that display the content which is similar to a portal screens. These screens are designed and published by using the ABAP language. these are called WEB Dynpro. ABAP pages 9WdA). The major intension is get away from JAVA WEB Dynpro pages. It is also referred as UI (User Interface)
5) SAP Fiori Launchpad:
SAP fiori is a new user experience (UX) for SAP software. By applying modern design principles it completely reinvents the user experience. It provides personalised and role based the new user experience enables enterprised wide engagement across lines of business. It provides optimal usability on multiple devices for better business interactions and ease of use.
6) SAP Web Interface (Java applications):
These screens are defined in JAVA and they are called as WDJ (Web Dynpro Java). JAVA based SAP products are replaced by using Web Dynpro ABAP.
Presentation Layer
Presentation Layer:
It is the layer where user submits the request using an interface. Like command line interface, graphical user interface, web interface or mobile interface or any other devices, etc.
It is a small software that is used to communicate with application server. It requires inputs such as port, protocol, host name etc.
Protocol: It is used to govern the data transmission between systems.
Port: It is a terminating point to access the application.
These both are maintained in the file /etc/services.
Hostname / IP Address: It is unique in thelandscape. The naming conventions of the hostname can be global (google.com / yahoo.com) or local.
Each hostname is assigned to an IP address. These are maintained in /etc/hosts or in company DNS server or in a public DNS server (google/yahoo).
It is the layer where user submits the request using an interface. Like command line interface, graphical user interface, web interface or mobile interface or any other devices, etc.
It is a small software that is used to communicate with application server. It requires inputs such as port, protocol, host name etc.
Protocol: It is used to govern the data transmission between systems.
Port: It is a terminating point to access the application.
These both are maintained in the file /etc/services.
Hostname / IP Address: It is unique in thelandscape. The naming conventions of the hostname can be global (google.com / yahoo.com) or local.
Each hostname is assigned to an IP address. These are maintained in /etc/hosts or in company DNS server or in a public DNS server (google/yahoo).
SAP Transaction Codes & Use of Code
Transaction Code: It is shortest code to navigate to the SAP programs and reports which are long and confusing German names. These are displayed in Transaction code "SM01" and stored in table TSTC.
| S.No | ||
| 1 | SM51 | Monitoring the SAP servers overview |
| 2 | SM50 | Monitoring the work process overview |
| 3 | SM66 | To monitor the work process globally |
| 4 | SM04 | To monitor the user logged in locally |
| 5 | AL08 | To monitor the user logged in globally |
| 6 | SM12 | To monitor the locks held in the system. |
| 7 | SM13 | To monitor updates held in system. |
| 8 | SM14 | To monitor updates administrations. |
| 9 | SM21 | To monitor system logs. |
| 10 | ST22 | To monitor the ABAP system dumps |
| 11 | SM01 | To monitor the transaction locks |
| 12 | SM02 | Populating the messages during downting |
| 13 | ST01 | To monitor and switching the traces |
| 14 | ST02 | To monitor the SAP application buffers |
| 15 | ST03 | To monitor workload overview |
| 16 | ST04 | To monitor database buffers |
| 17 | ST05 | To monitor performance traces |
| 18 | ST06 | To monitor the OS statistics |
| 19 | ST07 | To monitor the applications load |
| 20 | ST11 | To monitor the developer traces |
| 21 | SM20 | To monitor the security audit logs |
| 22 | SM36 | Scheduling background jobs |
| 23 | SM37 | To monitor background jobs |
| 24 | SM35 | To monitor batch inputs |
| 25 | SM59 | Define the RC Connections |
| 26 | SM58 | To monitor the transactional Rfc |
| 27 | SMQ1 | To monitor the outbound queue |
| 28 | SMQ2 | To monitor the inbound queue |
| 29 | SP01 | To monitor spoold requests |
| 30 | SMMS | To monitor message server |
| 31 | SMGW | To monitor gateway |
| 32 | DB02 | To monitor databse growth |
| 33 | DB13 | To monitor database calender (Scheduling backups) |
| 34 | DB12 | To monitor database logs |
| 35 | DB01 | To monitor database locks |
| 36 | DB17 | To monitor database checks |
| 37 | WE05 | To monitor Idocs |
| 38 | AL11 | To monitor SAP directories |
| 39 | DB14 | To monitor the database operational logs |
| 40 | DB03 | To monitor the parameter change in database |
| 41 | SMICM | To monitor the internet communication manager |
| 42 | SITSPMON | To monitor the internet transaction server |
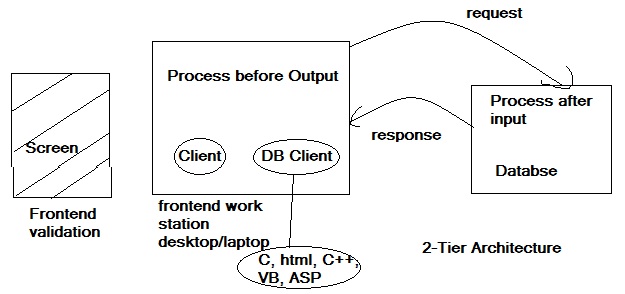
SAP : 3-Tier Architecture:
Application Server/Layer/Tier:-
It is introduced between client and server to address the above Issues (Two Tier Architecture)
- The User submit the request using SAPGUI using application server Host Name and Instance number (Port)
- The requests are received by the dispatcher and kept in the wait queue.
- Dispatcher maintains the work processes and identifies the load handled by Processes.
- The dispatcher allocates a freely available process to the user request based on FIFO(First In First Out)
- The work process contains inbuilt task handlers to interpret the request. The user context rolled into WP(Work process) task handler.
- The screen in the user request is interpreted by screen handler (interpreter)
- The Programming language in the user request is Interpreted by ABAP Handler (Interpreter)
- The SQL Scripts (Commands) in the user request are interpreted by SQL Handler (Interpreter)
- The request checks whether the content is available in R3Buffer. R3Buffer is used to store the most frequently used content and less frequently modified(updated) content.
- If the response is not available in R3Buffer then the process goes to the database using DB Specific client and SAP Kernal (OS and DB Specific)
- Database provides the response to the SAP work process after necessary interpretations.
- The SAP work process checks whether the response (Content) is eligible for buffering, so that a copy can be kept in R3Buffer for future similar requests.
- The work process roll out the user related information into user context. User Context: It is a small memory area where the user related information is stored. It contains user authorisations, parameters, common user attributes etc.. R3Buffer builds when the instance (application server) is started and R3Buffer is lost when the application server stopped.
- The response is sent to user.
- Roll-in: It is the process of copying the user context into WP task handler. When user is logging for the first time the Roll-in is not available.
- Roll-Out: It is the process of copying the user specific information into user context while sending the response to the user by a process.
- Kernal: Set of executable, binaries and libraries to communicate with OS, DB and Hardware.
- DB Client: Set of executable, binaries and libraries to communicate with the database in the native languages.
Port is derived from a two digit instance number where SAP application server is installed.
Instance number is a two digit ID which ranges between 00 - 99 (where 97, 98 & 99 are reserved)
The Host names and ports are resolved either from /etc/hosts and /etc/services. Most of the companies uses DNS Server for name resolution.
Protocol: It is
used to monitor the data transmission between the systems tcp/ip is a base
protocol which is used to derive further protocols. Set of rules that Governs
transmission of data.
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
FTP – File Transfer
Protocol
SMTP - Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol
HTTP – Hyper Text
Transfer Protocol
HTTPS -
Secured Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (using SSL)
SOAP - Simple Object
Access Protocol
WAP - Wireless Application
Protocol
Port: It is a
terminating/accessing/entry point to access the software/device/application.
http : 80/800
https : 443
SMTP : 25
ftp : 21
The port number ranges between 0-65535. The application
reserves the port number to avoid the port conflict. The ports and protocols
are maintained in file/etc/services
Server: The
system with high availability peripherals to serve the users is called a
server. The operating system distinguishes between desktop and server version.
This server version provides a robust, scalable, consistent
and reliable platform to host the applications, data bases etc.
Domain server:
Used to host the domain in the company.
File server: It
is used to provide file storage services in the company.
Mail server: Used
to provide mail services for communication from internal and external users.
FTP server: Used
to upload the files.
DHCP server: Used
to release and renew IP addresses for all the systems that log on to the
domain.
Web server:
Provides web services in a company.
Print server:
Used to host all the printers and provide collaborative print facilities to the
users.
Client: It is a
system which is used by end users to communicate with the servers.
Client can be a desktop/laptop/webtop/ device with installed
software to communicate with server.
Ex: MS Outlook, outlook Express, internet Explorer, lotus
notes, SAPGUI etc.
Client is software which contains a set of commands
programs, executables, libraries that are used to communicate with servers. He
is also referred as frontend to communicate with backend. Client requests and a
server Responds. Client is referred as it service requester and server is
referred as request processor. In a client server communication the clients are
overloaded along with servers due to the following reasons.
- There is no queue mechanism to process the request. The server has to handle the queue explicitly.
- There's no inbuilt interpreters (client and server has to interpret separately). No intermediate interpreters.
- There are no intermediate buffers/cache to reduce hits on the server. Every request hits server.
- Every client is required DB client to communicate with server. There is a need to deploy and intermediate layer to address the above issues.
The above architecture is also referred as two tier
architecture.
Introduction to Host name & IP
Host name: Which
system in the data centre is identified by unique name which is called as host
name without host name the system could not be communicated over Network.
IP address:
Internet protocol address: It is a numeric cable assigned to each machine that
is going to participate in the network communication.
Private IP addresses:
These are used internally within the company. It ranges between 0-255, 0-255,
0-255, 0-255. (4 bit).
A class IP address starts with 10.0.0.1 (Big companies uses
this range)
B class IP address starts with 172.17.0.1 (Middle sized
companies uses this range)
C class IP addresses starts with 192.168.0.1 (Small sized
companies mostly R&D)
Other than the above all the address are public IP
addresses. These IP addresses are obtained from network carriers.
Static IP address:
The addresses that is assigned to servers permanently so that addressing to the
server is constant.
Dynamic IP address:
The addresses that are assigned dynamically which can be renewed for every
14 days based on DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). These are assigned
to all desktops/ laptops/ workstation/Devices.
Intranet: The
computers which are connected outside the company network using MAN (Metro Area
Network)/WAN (Wide Area Network) using public IP address.
Router: It is a
physical device that is in entry/exit point to the network. Router can be set
with predefined rules.
Firewall: It is a
Software/Hardware/Server that is used to restrict/prohibit the access to
websites, IP addresses, host names, ports and protocols.
Various types of Operating systems
Operating Systems are
various types:
GUI (Graphical User Interface): Most
of the operating systems are windows based and currently Linux operating
systems like SUSE/RHEL/CENTOS/OLES.
CLI (Command Line interface): CLI are
more secured operating systems as most of the viruses are designed for
executables. CLI OS version works based on Libraries and Scripts. AIX, HP -
Unix and Oracles SUN Solaris.
haracter based Operating
systems: These are also command line interface operating systems but worked
based on characters and numbers. Easy to operate and navigate to the system.
Ex:
AS400/OS400
Memory
Memory: It is
used to perform the calculation/data manipulation. It is temporary work area.
The data on the memory will be lost when is system is powered off. Volatile
memory is computer storage that only maintains its data while the device is
powered. Mostly RAM is used for primary storage in personal computer which is a
volatile memory. To provide high availability the memory is inserted into different
slots. (don't buy 32 GB RAM sticks instead 4 sticks of 8 GB is recommended).
Memory is measured in megabytes(MB), gigabytes(GB).
Computer storage:
The data is stored in BITS and bytes. (bits are 0 & 1)
8 bits = 1 byte
1024 bytes = 1 KB (Kilobyte)
1024 KB = 1 MB (Megabyte)
1024 MB = 1 TB (Terabyte)
1024 TB = 1 PB (Petabyte)
1024 PB = 1 Exabyte
1024 Exabytes = 1 Zettabyte
1024 Zettabytes = 1 Yottabyte
1024 Yottabytes = 1 Brontobyte
1024 Brontobytes = 1 Geopbyte
1024 Zettabytes = 1 Yottabyte
1024 Yottabytes = 1 Brontobyte
1024 Brontobytes = 1 Geopbyte
Storage: Storage
it is used to store the data consistently and it is non volatile. It is
measured in GB, TB etc. Disc performance
depends upon the disc speed rpm (revolutions/rotations per minute).
5600/7200/10000/15000 rpm. Servers generally use 15000 rpm and laptops uses
5600 rpm.
Hard disc of various
types: IDE, SCSI, SATA, SAS.
To get more performance (IOPS - input output per second)
(eye OPS) by more than a single disc.
Ex: 1TB disc is not recommended instead 300 GB x 4
are recommended which will be also used for fail over.
Network cord: It
is a gateway for the computer to communicate with external world. It is used to
provide connectivity with external systems. It would be either LOCAL, WIDE,
METRO AREA NETWORK (LAN/WAN/MAN) to provide high availability more than one
network cord is installed.
Each network cord he is unique and contains its own MAC (Media
Access Control) address.
System: The
collaboration of CPU, memory, disc and Ethernet code plugged on to your mother
board is referred as a system.
The system is identified by its unique name referred as host
name. The hostname details are maintained in a file/etc/hosts. The system is
hardware which requires software to operate it.
Operating system:
It is a set of commands, libraries, executables which are programmed in C, C++,VC++
and java etc.
Friday, August 5, 2016
Data transfer
techniques: SAP supports various data transfer techniques to transfer the
legacy, parallel processing data into SAP System. It support various interfaces
to communicate with SAP and Non-SAP System.
Continuous Support:
SAP provides continuous improvement to existing software by releasing patches,
packages, support stacks, upgrades and enhancement packages etc.
Best practices /
Business Configuration sets: SAP provides are configured scenarios,
solutions, building blocks and best practices to accelerate the implementation
of SAP. Global best practices reduced cost, risk time.
High availability: It
supports all the high availability services of cluster / backup / restore / recovery / standby
and disaster recovery solutions.
Optimal response
time: It provides optimal response time of 600millisonces to 2 seconds for
each step (request through a mouse – click/keyboard stroke like f1, f2, f5, f8
and Enter.
Business Innovation: SAP
provides my SAP Business suite business innovations 2011 which comprises of SAP
ERP (SAP enterprise resource planning), SAP SRM SAP suppliers relationship
management), SCM (supply chain management).
Netviewer: SAP
provides a common platform netweaver to install all the required components in
a single system (enterprise portal, exchange infrastructure, business
intelligence, mobile infrastructure development. Infrastructure can be
installed along with ERP system at one step).
Risks:
- OS/ DB/SAP compatibility with hardware
- OS and Hardware Enterprise
- Network bandwidth and data transfer rate
- SAP support licensing and compatible software
- Onsite and Offshore communication
- Existing data centre team support and availability
- Take backup and restore capability
Hardware: It is a
computer hardware in that facilitate various input and output devices to handle
the user request and display or output the response to a monitor or printer.
CPU (Central
Processing Unit): It is used to process the request by allowing a dedicated
or shared process ID/thread ID to the user. The processor power is measured by
using mhz/ghz to provide high availability dual/ multiple CPU all installed for
failover and load balancing.
Each vendor CPU speed differs from model to model (DELL,
IBM, HP)
- CPU can be monitored on windows by using task manager
- CPU is monitored on Linux by using command "top"
- CPU is monitored in SAP system by using transaction "ST06"
- CPU fetches the data into memory and holds as long as it is committed or rollback
License Fees:
License Fees: SAP Supports a small, midsized and large enterprises and cut down the license cost to reach the customers (ex: each user costs around 2,00,000 INR which has been reduced to 60,000 INR) based on number of users, location, business and volume of licensing etc.
SAP Independency
SAP – System Applications and Products
1. OS Independent
2. DB dependency
3. Language Independent
4. Rich set of modules
5. Business functions
6. Inbuilt web functionality
7. Mobile Infrastructure
8. Analytics and Reporting
9. SAP Support
10. SAP Security
Efficient:
Update Integration:
1. OS Independent
2. DB dependency
3. Language Independent
4. Rich set of modules
5. Business functions
6. Inbuilt web functionality
7. Mobile Infrastructure
8. Analytics and Reporting
9. SAP Support
10. SAP Security
Efficient:
- It is user friendly anyone can learn it quickly and it is easy to operate.
- Its design enables user to enter data without difficulty and its control functions significantly decreases the occurrence of mistakes in data entry and the forwarding of incorrect data.
- Allows easier global integration (barriers of currency exchange rates, language and culture can be bridged automatically)
Update Integration:
- Updates only need to be done once to be implemented company wide.
- Vendors have past knowledge and expertise on how to test build and implement a system.
- User interface is completely customizable allowing end users to decate the operational structure of the product.
Data Redundancy:
- Provides real time information reducing the possibility of redundancy errors.
- May create efficient work environment for employees.
OS Independency:
- SAP is operating system independent
- Microsoft – Windows
- IBM – AIX, Main frames, IBM AS 400/1 Series
- HP – Unix
- Sun Solaris from Sun Micro Systems (Sun is taken over by Oracle)
- Linux (Cent OS, Fedora, RHEL, SUSE Linux and ORACLE Linux)
- SAP can be installed on any of the operating system where as Microsoft Dynamics is SQL Server products are dependent on Windows Servers(Operating System)
- Oracle Could not be installed on AS400/Mainframes machine (AS400 comes with DB2)
DB Independency:
- SAP database independent
- Oracle from ORACLE Corporation
- DB2 from IBM
- MSSQL Server from Microsoft
- SAPDB (MAXDB)and Sybase from SAP
- Informix is available for older versions (Outdated now)
- SAP Adaptive Sybase enterprise edition (Sybase ASE)
- SAP HANA database from SAP
- SAP can be installed on any of the Databases where as Oracle Apps and oracle products are dependent on Oracle Database.
Language Independent: It is Unicode language system to support around 90,000 characters i.e. almost all the available 560 languages in the world.
By default English and German are available the additional languages are required to be installed as part of the past installation based on requirement.
Rich set of Modules: SAP contains rich set of modules (FI, CO, SD, MM, HR, PP, PS, WQM, PM and other function based on the requirement).
Execute “SPRO” to check all the default modules.
Business functions: Provides industry extensions (add-ons) industry specific solutions, such as oil, gas, mining, textile, campus management, chemicals, health care, media, energy, insurance banking etc.
Most of them are inbuilt in the system and requires additional licenses (payment) to use them.
These are accessed by using SFW5
Inbuilt Web functionality: SAP Support web infrastructure so that SAP systems can be accessed over the web without any additional software/hardware. It is inbuilt functionality and required one time activation.
Mobile Infrastructure: SAP support mobile infrastructure to communicate with external devices like PDA (Personal Digital Assistants) like palm tops, black berry, iphone, android, Motorola and other hand held devices.
Analytics and Reporting: SAP Supports Reporting functionality through inbuilt business intelligence system (BI/BW) at plat form level. It is used for Analysis/Reporting and decision making.
SAP Support: SAP supports the customer production environments 7X24X365 through global support centers located in Bangalore, Shanghai, Ireland and Singapore etc.
SAP Security: SAP provides role based, menu based, field level, org level security to protect the sensitive information of the customers/assets/employees/suppliers etc.
SAP Supporting: Supporting Hardware: fujitsu, seimons, CISCO, IBM SUN, DELL, HP
Supporting OS: Linux (Redhat, SUSE, Cohos, OLES), IBM – AIX, AS/400, Mainframes), HP (Unix), Microsoft (Windows), Sun(Solaris) *AI, AS/400 cannot be installed on oracle)
Supporting Databases:
- Oracle,
- IBM – DB2, DB4, DB6,
- HP - Informix,
- Microsoft - SQL Server,
- SAP – SAPDB, Sybase, HANA DB.
SAP Modules:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)